Industrial Ethernet in production
Ethernet has long been the current communication standard in IT. Over the past ten years, Ethernet has increasingly been used in the industrial environment. What are the reasons for this? And: Is Ethernet actually suitable for the high requirements in production?
Communication in industrial applications often poses requirements that do not play any role in office communications: Real time and determination are the decisive keywords here.
An E-mail or print order that arrives with a delay of half a second in an office environment is hardly an issue and will not lead to malfunctions. But such a delay is often not acceptable when controlling machines in an industrial environment. A reaction must occur here within a specified time. The most frequently used communication systems in industrial applications are therefore field buses, such as Profibus, CAN, etc., which can guarantee the necessary real time behavior.
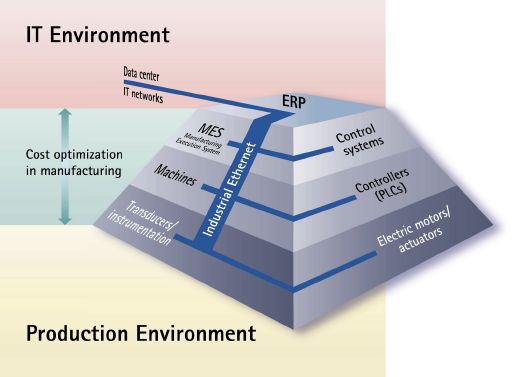
Different levels of communication systems
Communication systems in industrial applications can be divided into different levels:
- Field level
- Controller level
- Process control level
A frequent challenge posed by modern plants is universal communication from the process control level, where ERP systems are located for instance, down to the field level to the sensors and actuators.
At the process control level, communication via Ethernet is standard, so that efforts are being aimed at also processing communication within the lower levels using Ethernet. There have therefore been various approaches and solutions presented over the past ten years on how to provide real time capability, which is frequently required for machine and plant control, for communication via Ethernet.
Real time solutions for Ethernet
There are now a wide range of solutions available under the term Industrial Ethernet, such as Ethercat, Profinet, Ethernet/IP etc., that also offer real time capability for communication via Ethernet. Most of these different systems are supported by user groups who are in turn backed by large suppliers in the sector of industry automation.
However, the development of different systems, which are generally not compatible with each other, means that the simple interchangeability and interoperability seen in the sector of office communications is not achieved here.
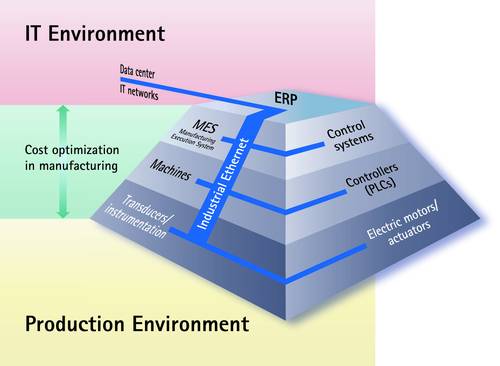
Even larger data volumes can be easily transferred
In addition to "universal" communication from the process control level to the field level, Industrial Ethernet has further advantages: The primary advantage is the very high bandwidth, compared to conventional field bus systems, that makes it possible to transmit even larger data volumes at high speed.
A universal system also offers great advantages with regards to maintenance, data backup and engineering, advantages that are generally linked with less outlay and therefore less costs. A system with open communication interfaces is also equipped for future applications. Enhancements can often be implemented without need for comprehensive modifications to the hardware.
The differences between Industrial Ethernet and "normal" Ethernet
Industrial Ethernet is not the same as "normal" Ethernet. What are the differences between the technologies?
The various solutions for real time-capable Ethernet use protocols, components and topologies that, in part, are significantly different from conventional Ethernet. But it is not just the different mode of functioning, due to real time capabilities, that is decisive in components used in the industrial environment, for example a switch.
All the other ambient conditions that are present, for example, during production, also have to be tolerated at the same time. The components must be designed for the sometimes significant stresses caused by dust, humidity, higher temperatures, shocks and vibrations.
Large data volumes, fast connections, secure results: Various points have to be considered in the interaction between measurement technology, industrial automation and Industrial Ethernet.
Measurement technology is frequently used – in machines and plants – during industrial production processes. The spectrum here is extremely diverse, ranging from simple signals acquired with low frequencies - for example, slowly changing temperature values - right up to complex measurement data, which need to be measured using higher measurement frequencies.
Industrial Ethernet and Measurement technology in industry
Ethernet enables fast connections
A fast connection, as offered by Ethernet, is a great advantage, especially in applications where very large data volumes occur during measurement. If the measurement technology used needs to be integrated in a higher-level control architecture, for example, based on PLC, the hardware used needs to provide the appropriate communication options.
In applications where large data volumes occur and where real time is also a necessity, then solutions based on Industrial Ethernet are suitable.
The manufacturers of measurement technology components and systems have therefore been offering interfaces to various Industrial Ethernet solutions for some time now. The general trend that can be seen here is that classic measurement technology systems on the one side and automation solutions on the other side are coming together at an increasing rate.
Measurement technology taking over automation tasks
Modern industrial measurement technology systems are now also capable of taking over automation tasks. In addition to controlling the measurement sequences, such modern systems can also control the machines. Industrial Ethernet also offers possibilities in the sectors of remote maintenance and operation. Numerous measurement technology systems can be operated using a standard web browser. The measured data can therefore be displayed over the Internet with practically no limitations.
Enjoy the advantages of Industrial Ethernet - with PMX, the industry standard for measurement technology.