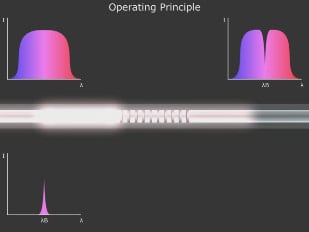
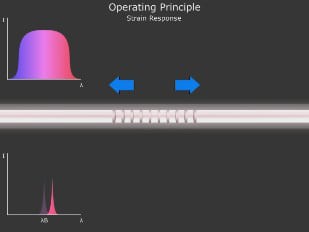
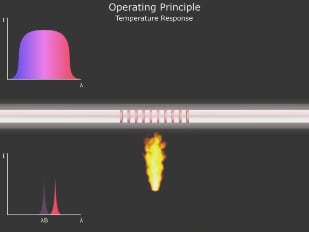
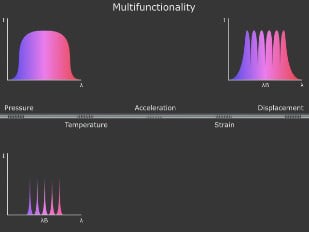
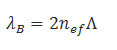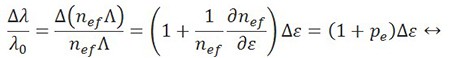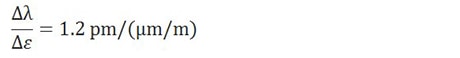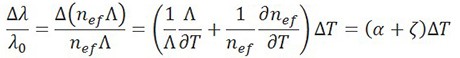A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a microstructure typically a few millimeters in length that can be photo inscribed in the core of a single mode fiber. This is done by transversely illuminating the fiber with a UV laser beam and using a phase mask to generate an interference pattern in its core. This will induce a permanent change in the physical characteristics of the silica matrix (fig. 1). This change consists in a spatial periodic modulation of the core index of refraction that creates a resonant structure.
Protected with a primary coating, the diameter of the fiber is 250 micrometers. Without this coating, the fiber has a diameter of 125 micrometers. The light then travels within the core, which has a diameter of approximately 8 micrometers.