The system architecture
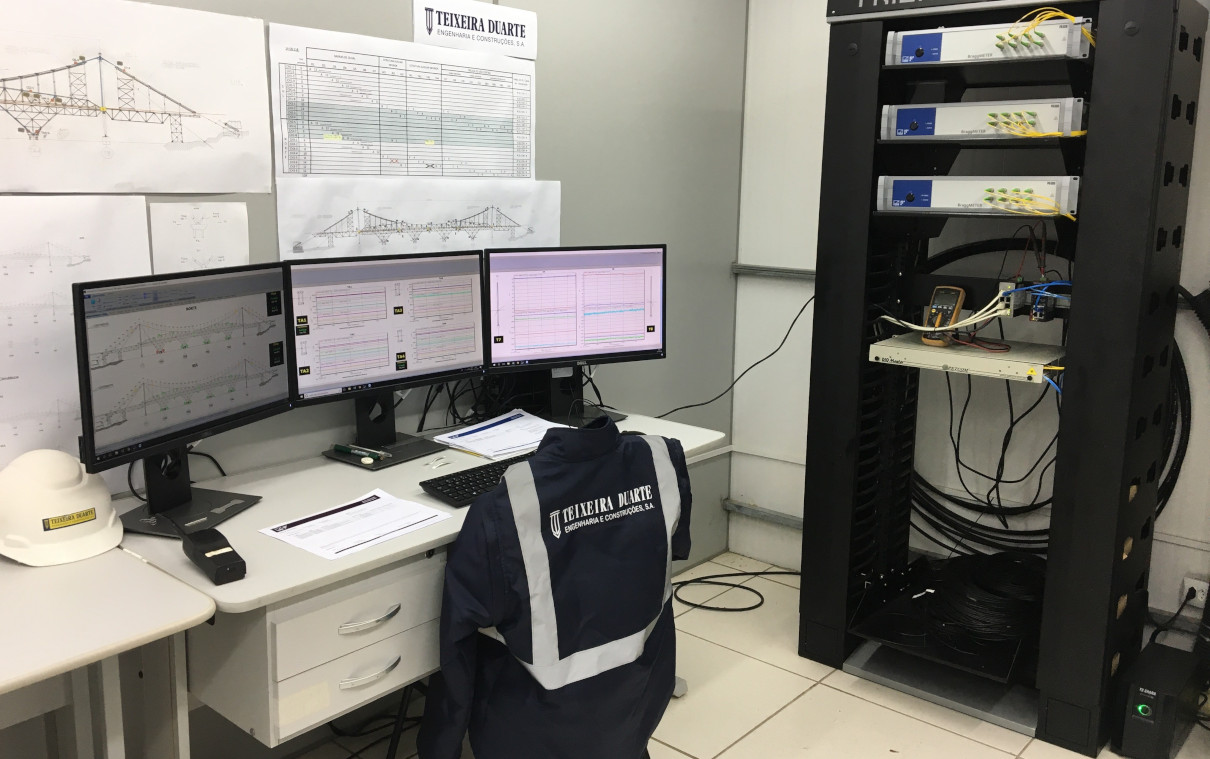
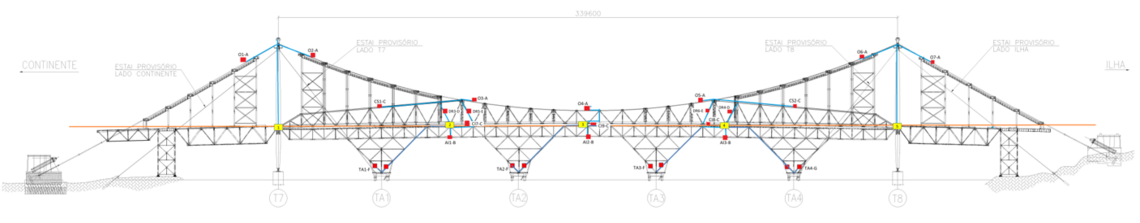
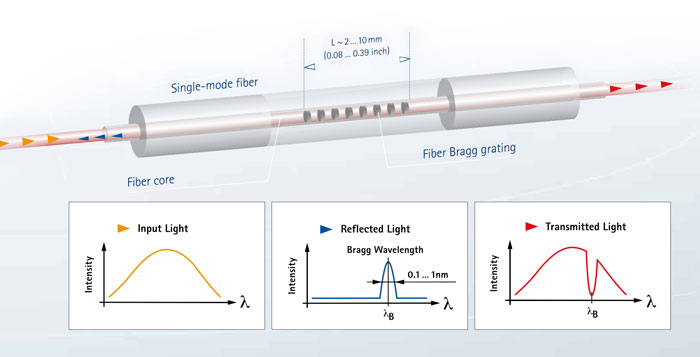
For the instrumentation of the bridge structure, a hybrid architecture was defined, one that uses both optical sensors based on Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) and conventional electrical sensors for various quantities. The measurement of deformations, temperature, wind speed and sea currents are part of the global monitoring system. In total, 284 optical sensors were acquired by 3 HBM FiberSensing interrogators. Taking advantage of the optical network necessarily installed for the transmission of signals from the optical sensors, the communication of the HBM's PMX was integrated to read the electric sensors in the two 24-way multifiber cables, deployed along the 800m of the bridge.
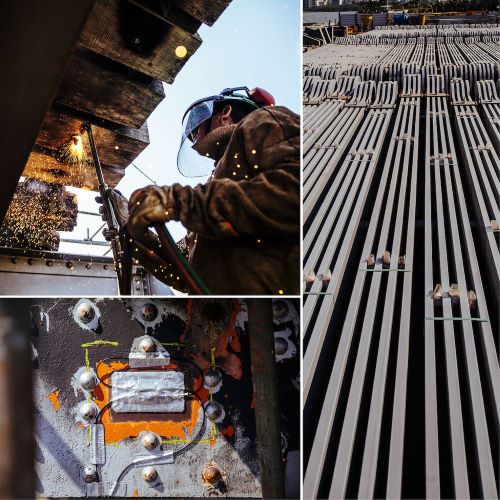
At strategic points for sensor connection, the multifiber cable has been bled to individually connect each fiber to the sensors. All connections were protected by dedicated boxes along the structure.
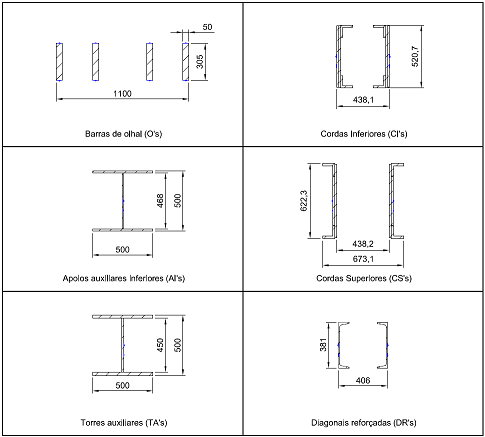
For ease and speed of the installation process, an essential requirement for the project execution, the optical sensors were delivered as pre-assembled sensor chains. Two different methods for sensor installation were chosen depending on the structural parts where they would be placed. Since the bridge is a metal structure, the most obvious choice was that of spot welding sensors. For the central trusses and auxiliary supports - parts that remain in the structure during the whole project - this was the chosen form of installation. For the eye-bars - the parts to be replaced - glued sensors were selected. Sensor chains included strain and temperature sensors. The combination of the two is needed to compensate for temperature effects on strain measurements.